Introduction:
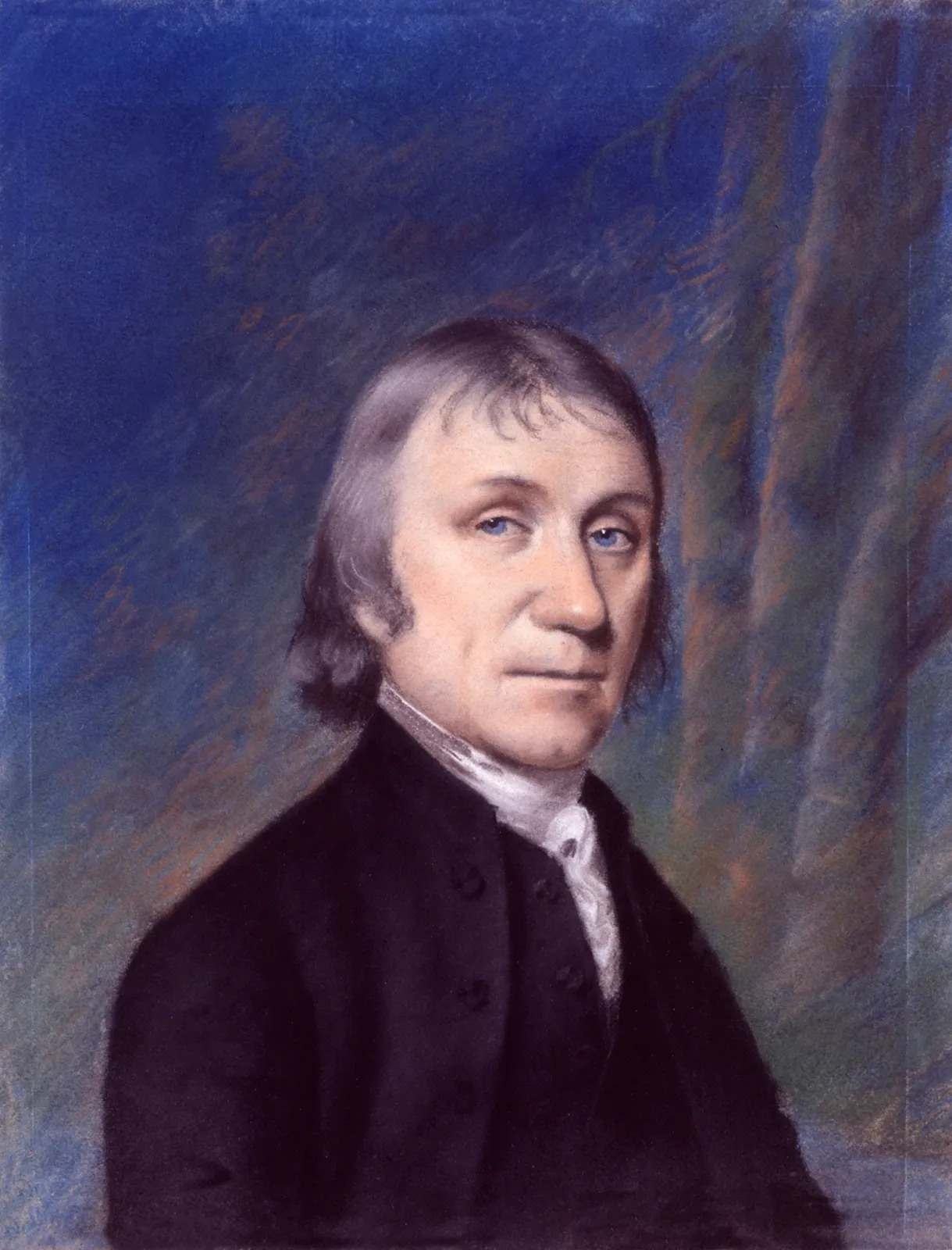
In the annals of scientific history, few discoveries have been as fundamental and transformative as the identification of oxygen. At the heart of this groundbreaking revelation stands Joseph Priestley, a polymath whose pioneering experiments unlocked the secrets of this vital element. In this blog, we embark on a journey through Priestley’s life and work, tracing his remarkable contributions to science and his enduring legacy as the man who unraveled the mystery of oxygen.
1. Early Life and Education:
Joseph Priestley was born on March 13, 1733, in Birstall, Yorkshire, England. From a young age, he displayed a keen intellect and insatiable curiosity, traits that would shape his future endeavors. After receiving a rudimentary education at local schools, Priestley pursued further studies at Daventry Academy, where he honed his skills in languages, theology, and natural philosophy.
2. Scientific Exploration:
Priestley’s scientific journey began in earnest during his tenure as a minister in various English towns. Inspired by the spirit of inquiry and the scientific revolution sweeping Europe, he devoted his spare time to conducting experiments and observations in diverse fields, including chemistry, physics, and electricity. His inquisitive mind and innovative approach set him apart as a rising star in the scientific community.
3. Discovery of Oxygen:
The crowning achievement of Priestley’s scientific career came in 1774 when he made the groundbreaking discovery of oxygen. Through a series of meticulous experiments involving the heating of mercuric oxide, Priestley isolated a new gas with remarkable properties. Unbeknownst to him at the time, this gas would later be recognized as oxygen, laying the foundation for our modern understanding of chemistry and physiology.
4. Collaboration with Antoine Lavoisier:
Priestley’s discovery of oxygen sparked a revolution in chemistry, igniting a flurry of research and debate among scientists across Europe. Among those captivated by Priestley’s findings was French chemist Antoine Lavoisier, whose own experiments confirmed and expanded upon Priestley’s observations. Despite their disparate backgrounds and nationalities, Priestley and Lavoisier forged a fruitful collaboration that helped elucidate the nature of oxygen and its role in combustion and respiration.
5. Controversy and Criticism:
Priestley’s revolutionary ideas and outspoken advocacy for scientific inquiry often brought him into conflict with established authorities, both within the scientific community and in broader society. His support for radical political causes and religious dissent further fueled controversy and subjected him to persecution and censorship. Despite facing considerable opposition, Priestley remained steadfast in his commitment to truth and intellectual freedom.
6. Legacy and Impact:
Joseph Priestley’s discovery of oxygen ranks among the most significant milestones in the history of science, reshaping our understanding of the natural world and laying the groundwork for modern chemistry and biology. Beyond his contributions to science, Priestley’s legacy endures as a testament to the power of curiosity, perseverance, and independent thought in the face of adversity. His life and work continue to inspire scientists and scholars around the world, reminding us of the transformative potential of scientific inquiry.
Conclusion:
In the pantheon of scientific luminaries, Joseph Priestley occupies a place of honor as the man who unlocked the mystery of oxygen and forever changed the course of human knowledge. His journey from humble beginnings to scientific renown serves as a testament to the transformative power of curiosity, ingenuity, and perseverance. As we reflect on Priestley’s life and legacy, we are reminded of the boundless potential of the human mind to unravel the mysteries of the universe and shape the destiny of humanity.