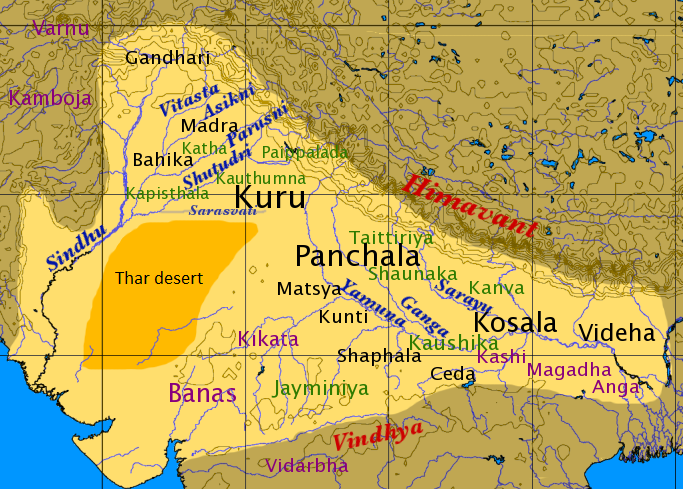
Nestled in the heartland of ancient India, the Panchala kingdom emerges as a storied realm of valor, culture, and political intrigue. From its mythical origins to its historical prominence, the saga of Panchala unfolds as a captivating tale of dynastic power, artistic patronage, and enduring legacy. In this exploration, we embark on a journey to unravel the enigmatic history of the Panchala kingdom, tracing its origins, delving into its cultural milieu, and examining its lasting impact on the annals of Indian history.
1. Mythical Origins and Early History:
The origins of the Panchala kingdom are steeped in myth and legend, intertwined with the narrative of ancient Indian texts such as the Mahabharata and the Puranas. According to traditional accounts, the kingdom was established by King Drupada, a legendary ruler descended from the lunar dynasty. Over time, the Panchalas emerged as a formidable political force in northern India, wielding influence over vast swathes of territory.
2. Cultural Milieu and Artistic Patronage:
At the heart of Panchala culture lay a rich tapestry of artistic patronage, intellectual inquiry, and spiritual devotion that underscored the kingdom’s identity. The Panchalas were renowned for their patronage of the arts, including music, dance, literature, and architecture. The royal court of Panchala served as a vibrant hub of cultural exchange, attracting scholars, poets, and artists from far and wide.
3. Dynastic Rivalries and Political Intrigue:
The history of the Panchala kingdom is punctuated by dynastic rivalries, political intrigue, and power struggles that shaped its destiny. The rivalry between King Drupada and his cousin Drona, as depicted in the Mahabharata, serves as a poignant example of the kingdom’s internal conflicts. Despite its internal divisions, the Panchala kingdom continued to exert influence on the political landscape of ancient India, forging alliances and rivalries with neighboring powers.
4. Role in the Mahabharata Epic:
The Panchala kingdom occupies a central place in the narrative of the Mahabharata, one of the world’s longest epic poems. The marriage of Princess Draupadi, the daughter of King Drupada, to the Pandava princes serves as a catalyst for the epic’s unfolding drama. The city of Kampilya, the capital of Panchala, becomes a pivotal setting for key events in the Mahabharata, including the Rajasuya sacrifice and the game of dice.
5. Decline and Transformation:
Like many ancient kingdoms, the Panchala kingdom eventually faced challenges to its authority and supremacy. Dynastic conflicts, external invasions, and socio-political upheavals precipitated the decline of the kingdom, leading to its eventual absorption into larger political entities. The rise of regional powers such as the Magadha and Kosala kingdoms signaled the end of Panchala’s political dominance, though its cultural and artistic legacy endured.
6. Enduring Influence and Legacy:
Though the Panchala kingdom may have faded into obscurity, its legacy endures as a cornerstone of Indian civilization and artistic expression. The Panchalas’ contributions to literature, music, dance, and architecture continue to inspire artists and scholars to this day. The kingdom’s role in the Mahabharata epic ensures its place in the pantheon of Indian mythology and literature, preserving its memory for future generations.
Conclusion:
In the annals of Indian history, the Panchala kingdom stands as a testament to the enduring spirit of artistic patronage, cultural vibrancy, and dynastic power. From its mythical origins to its historical prominence, the saga of Panchala resonates with echoes of bygone eras and vanished kingdoms. As scholars continue to unravel the mysteries of Panchala’s legacy, they illuminate the rich tapestry of Indian civilization and the timeless quest for cultural flourishing and artistic expression.